Like France, Spain is a country whose history and culture are closely linked to viticulture.
Among the many Spanish wine regions, Rioja occupies a prominent place in particular. Nestled in the north of the country, the eponymous appellation is indeed very renowned for its red wines elegant and complex . However, it also produces, albeit in small quantities, white wines And rosés of quality.
In this article, we will therefore explore Rioja in depth, examining its history, its wines, its climate, its terroir , as well as the differences that the region presents compared to its illustrious neighbor, the Ribera del Duero. We will also look at the food and wine pairings ideals with local vintages.
Have a nice trip ! (Have a good trip)
History of the Rioja appellation
The history of viticulture in Rioja dates back to Antiquity , when the Phoenicians, then the Romans introduced the vine into the region.
However, it was not until the Middle Ages, under the influence of monasteries and religious orders, that the vineyard really began to develop. Indeed, the first written mention referring to the vine in the region dates from 9th century of our era.
In the 13th century, the first wines from Rioja began to be exported beyond its borders. Then, from the 15th century onwards, regional trade began to focus significantly on viticulture.
Over the centuries, Rioja continued to gain in reputation, eventually becoming one of the first regions in Spain to establish rules for wine production in the 19th century.
A few decades later, in 1925 , the controlled designation of origin "Rioja" is officially created (DOC, Denominación de Origina Controlada) . This is one of the first of Spain . In 1991 , this one reaches the supreme status of Denominación de Origine Calificada (DOCa), a distinction awarded to only one other wine region in Spain : Priorat.
Today, the Rioja is probably the best-known Spanish wine appellation to the world.
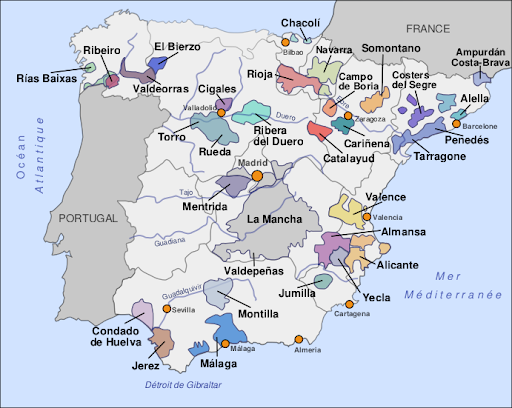
Map of the vineyards of Spain with Rioja in the center-north
DOCa Rioja wines
La Rioja is mainly renowned for its red wines . These latter represent in fact 90% of regional production and are mainly made from the grape variety Tempranillo .
Equipped with a medium acidity , Tempranillo presents a thick skin and distils aromas of red and black fruits (plum, prune, blackberry, blackcurrant, etc.), tobacco, chocolate and even pepper.
This allows the production of a whole typology of wines, ranging from fruity vintage to drink in its youth until great wine for laying down can improve over the decades. Aging in oak barrels (mainly American) is very common for this grape variety, bringing notes of vanilla, cinnamon, cloves, etc.
Representative 80% of regional grape varieties , Tempranillo is often associated with other complementary varieties such as the Grenache (Garnacha), the Mazuelo ( Carignan ), THE Graciano or even to the Maturana Tinta It is with these same 5 grape varieties that the rosés of Rioja are also produced.
But Rioja is also delicious white wines . The grape variety Viura is predominant for this color but other varieties are also planted like the Grenache blanc (Garnacha blanca), the Malvasia , THE White Tempranillo or even, although more rarely used, the Chardonnay and the Sauvignon . A total of 9 white grape varieties can be used.
Finally, some effervescent are also produced in the region and can be produced from the 14 grape varieties of the appellation.
Winemaking in Rioja
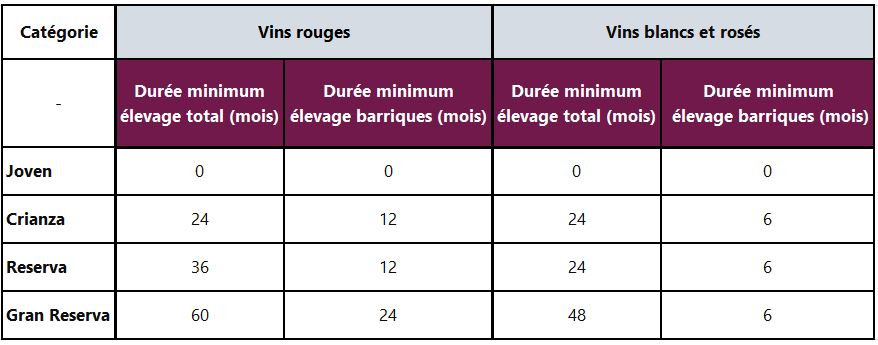
In Spain, wines can be classified into several categories according to their aging time in barrels and bottles. : Joven, Crianza, Reserva and Gran Reserva . Although these terms can be used throughout the country, Rioja has the specificity of having established an even more demanding specification for their use.
- Wines with the mention " Young » are young wines, little or no aging in barrels, and highlighting the freshness of the fruit . No minimum storage time in barrels or bottles is required here, whether for reds, whites or rosés.
- Red wines bearing the mention " Childhood » must be raised for at least minimum two years , including a minimum of one year in oak barrels. White and rosé wines with this designation must also be aged for a minimum of two years in total, including 6 months in barrels. Crianza wines therefore generally have fruity aromas but also notes of wooded .
- Red wines with the mention " Reserve » must undergo a minimum aging in barrels and bottles of minimum three years . Of these three years, at least one year must be spent in barrels, supplemented by 6 months in bottles. For whites and rosés, the minimum aging must be two years in total, including 6 months in barrels. The wines in this category are wines for laying down complex and have a great aromatic richness (fruity, woody but also tertiary notes such as leather, tobacco or truffle).
- Finally, red wines " Gran Reserva » represent the wine elite of the region and are only produced in the best vintages. These must undergo a minimum total aging of 5 years , including 2 years in barrels and 2 years in bottle. For whites and rosés, the total aging is 4 years minimum including 6 months in barrels. Regardless of their color, the "Gran Reserva" are great wines for storage presenting an incredible aromatic richness.
Summary table of the mentions of aging of Rioja wines
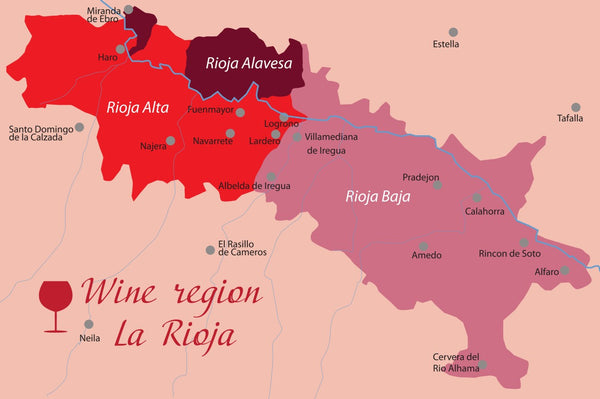
Climate and terroirs of La Rioja
The climate of La Rioja is of the type continental , characterized by hot, dry summers and harsh winters. Rainfall here is moderate and the temperature variations between day and night promote the optimal ripening of the grapes.
The appellation extends over more than 63,000 hectares within the provinces of Rioja, Alava and Navarre, and is divided into three main areas: Rioja Alta, Rioja Oriental (formerly Rioja Baja) and Rioja Alavesa .
- Rioja Oriental: Located in the east and also called Rioja Baja, this area has a hot and dry climate and has soils poor in nutrients. The wines produced here are the densest and most concentrated of the appellation.
- Rioja Alta: Located in the west, this region benefits from a cooler climate than Rioja Oriental, allowing the production of elegant wines with a beautiful acidity. The vines here are planted at an altitude of between 400 and 500m and the soils are clay-limestone.
- Rioja Alavesa: Nestled in the foothills of the Sierra Cantabria, this region enjoys a climate similar to that of the Rioja Alta but the wines are more intense, although still in finesse. The soils are rocky and the vines are also located between 400 and 500m above sea level.
The differences between Rioja and Ribera del Duero
La Rioja and the Ribera del Duero are the two flagship wine regions of Spain. Both located in the north of the country, they are therefore often compared and contrasted. However, while the two appellations share certain points in common, several factors differentiate them.
First of all, if Rioja and Ribera del Duero both have as identity grape variety Tempranillo (also called Fine Ink within the Ribera del Duero), the other varieties of the two regions are not common. Thus, if Grenache, Mazuelo and Graciano are used in Rioja, French varieties such as Cabernet Sauvignon , Merlot And Malbec are preferred within the Ribera del Duero.
In addition, the climate of The Ribera del Duero is much more continental than that of Rioja and is therefore characterized by much greater temperature extremes . La Rioja benefits from a certain oceanic influence which allows it to preserve freshness in its wines. As a result, The wines of Ribera del Duero are more powerful and denser than those of Rioja .
From a wine-making point of view, the estates from both regions almost systematically age their vintages in barrels. However, THE type of wood used to carry out these breedings is often different.Thus, within the Ribera del Duero, the French oak is mostly used, while in Rioja, wines are generally aged in contact with American oak , giving more pronounced spicy and exotic notes (vanilla, coconut, etc.).
As you will have understood, although certain common points unite the two vineyards, numerous differences build the uniqueness of the two appellations.
What to pair with Rioja wines?
Thanks to their aromatic diversity, Rioja wines are versatile and pair very well with a wide variety of dishes.
So, for a vintage stamped " Young » evolving mainly on the fruit, the poultry is an ideal agreement, just like a charcuterie board or even a roast of calf or ribs of pork with herbs.
For more powerful and complex wines such as Crianza, Reserva and Gran Reserva , there red meat then becomes an almost obligatory passage. The power and aromatic intensity of these vintages indeed impose dishes with a certain structure. Thus, prime rib, wild boar, pheasant or lamb chops will pair divinely well with this type of vintage.
Side cheeses , this time we recommend that you focus on the white wines or rosés from Rioja. Their structure and fruity notes will indeed go very well with Manchego , of Ossau-Iraty or even Beaufort or of County . Red wines can also be tried, but be careful. not to select bottles that are too tannic!
Finally, always with rosés and white wines, seafood, poultry and grilled fish will also go well together.

The best Riojas
As you will have understood, Rioja is a fascinating wine region which combines tradition and innovation to produce world-class wines.
If you want to explore it, there are many areas available to you, but we particularly recommend the Bodegas Muga , a big name in the region that stands out for producing exceptional wines. Their vintages provide an excellent overview of what Rioja has to offer. Complexity, elegance and ageing potential are all there !
Health ! And see you soon at The Illuminated Cellar !








